What is a Thermistor and what does it do ?

- Part No.:
- 103KT1608T-1P
- Manufacturer:
- Semitec USA Corp
- Category:
- Applications & Technologies
- Package:
- 0603 (1608 Metric)
- Datasheet:
-
 103KT1608T-1P.pdf
103KT1608T-1P.pdf
- Description:
- NTC THERMISTORS 10K OHMS 3435K 1% 0603
- Payment:

- Shipping:

Article Details
1. what is a thermister?
Thermistor is a generic term for Thermally Sensitive Resistor, a semiconductor component whose resistance value changes significantly with changes in temperature.
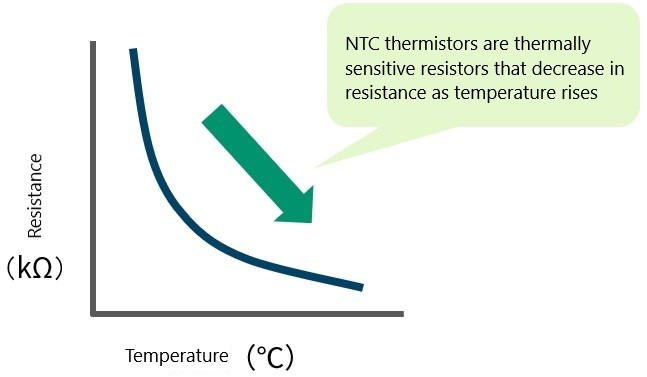
Those with a negative temperature coefficient, whose resistance value decreases with increasing temperature (see Figure 1), are called NTC thermistors.
Thermistors are ceramic semiconductors made mainly from metal oxides and sintered at high temperatures. Various characteristics can be obtained depending on the material used.
Because thermistor elements can be flexibly processed into a wide variety of shapes according to the application, they are widely used as temperature sensors for temperature measurement, temperature control, and temperature compensation in all kinds of equipment, including automobiles, home appliances, and medical devices.
2. What are the resistance / temperature chracteristics of thermistors?
The resistance value of thermistors varies greatly with temperature, and as shown in Figure 1, the relationship between temperature and resistance value varies exponentially.
The resistance / temperature chracteristics of a thermistor can be approximated by the relationship between resistance value and temperature over a certain temperature range as shown in Equation 1.
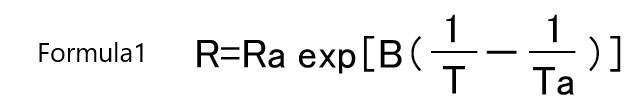
T, Ta: Absolute temperature (K)
R, Ra: Zero power resistance at T, Ta (Ω)
B: B value (K)
3. What is zero power resistance?
Zero power resistance refers to the resistance of a thermistor measured at a constant temperature and at a sufficiently low power consumption that changes in resistance due to self-heating can be ignored, and is denoted "R25". R25 indicates the zero power resistance at 25℃.
4. What is B value?
B value expresses the magnitude of change in resistance value obtained from the temperatures of any two points in the resistance / temperature chracteristics, and is expressed by Equation 2.
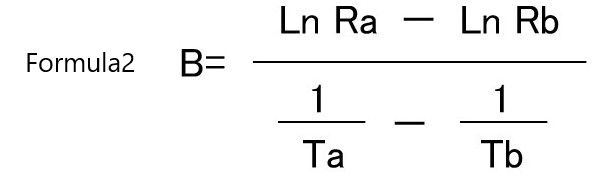
Ta, Tb: Absolute temperature (K)
Ra, Rb: Zero power resistance at Ta, Tb (Ω)
B: B value (K)
When this characteristic is graphed with IogR and 1/T, it can be expressed almost linearly.
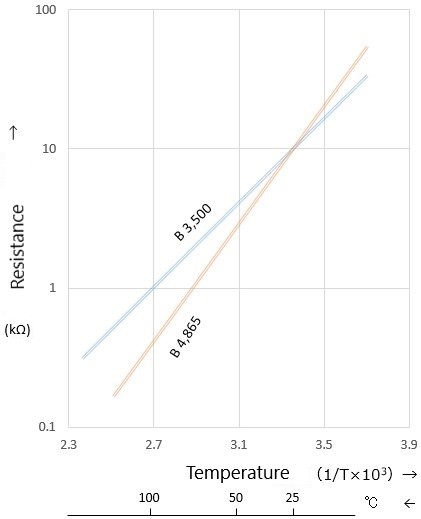
B value is denoted "B25/85," where B25/85 indicates the value calculated from the resistance value between two points, 25℃ and 85℃.
The larger B value, the larger the slope of the graph, which means that it is easier to detect small temperature changes and is more sensitive to temperature changes.
5. What is the heat dissipation constant?
The heat dissipation constant represents the power required to raise the temperature of a thermistor element by 1℃ in thermal equilibrium through self-heating. It is obtained by the ratio of the power consumption of the thermistor to the temperature rise of the element.
If the power consumption of a thermistor is P(mW), the heat dissipation constant is obtained by Equation 3.
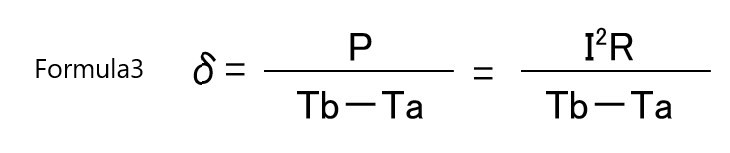
δ: Heat dissipation constant (mW/℃)
Ta: Ambient temperature of thermistor (℃)
I: Current flowing through thermistor (mA)
Tb: Temperature of the thermistor when the thermistor rises in temperature and reaches thermal equilibrium (℃)
R: Thermistor resistance value at Tb(℃) (Ω)
The heat dissipation constant is determined by the material, structure, and size of the thermistor.
When using thermistors for temperature measurement, it is advisable to keep the applied power as low as possible to avoid errors in the measured temperature.
6. What is the thermal time constant?
The thermal time constant expresses the time required for the temperature of the thermistor element to change by 63.2% between the initial temperature and the final temperature attained when the ambient temperature of the thermistor is suddenly changed under a zero load condition.
When the thermal time constant (τ) is multiplied by n, the rate of change of the temperature difference is as follows, which means that 95% of the temperature difference changes in about 3 times the thermal time constant.
τ= 63.2% 2τ = 86.5% 3τ = 95.0%
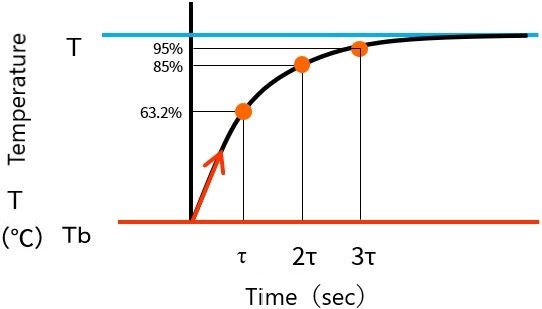
The smaller the thermal time constant, the faster the response speed with respect to temperature change.
103KT1608T-1P Specifications
- Attributes
- Property Value
- Manufacturer
- Semitec USA Corp
- Series:
- KT
- Package/Case:
- 0603 (1608 Metric)
- Packaging:
- Tape & Reel (TR)
- Product Status:
- Active
- Resistance in Ohms @ 25°C:
- 10k
- Resistance Tolerance:
- ±1%
- B Value Tolerance:
- ±1%
- B0/50:
- -
- B25/50:
- -
- B25/75:
- -
- B25/85:
- 3435K
- B25/100:
- -
- Operating Temperature:
- -40°C ~ 125°C
- Power - Max:
- 4.5 mW
- Length - Lead Wire:
- -
- Mounting Type:
- Surface Mount
- Grade:
- -
- Qualification:
- -
- Category:
- Applications & Technologies
The Posts

-
What is a Thermistor and what does it do ?
SEMITEC NTC Thermistor;MURATA NTC Thermistor;TDK NTC Thermistor;SUNLORD NTC Thermistor;AVX NTC Thermistor;Littelfuse NTC Thermistor

-
SEMITEC NT & GT Comparison Chart
Bomkey Electronics is the authorized distributor for the full range of SEMITEC products !SEMITEC's GT Series was officially discontinued in December 2017, with the NT Series serving as its replacement…

-
103AT-2:Bomkey Electronics offer the SEMITEC temperature sensors and NTC thermistors Resistors
As a distributor of SEMITEC products, Bomkey Electronics provides competitive pricing and real-time availability-contact us for details The AT series thermistor (Thermally Sensitive Resistor) features …

-
LR44 vs 357 Battery: Differences, Interchangeability, and How to Choose
When shopping for button batteries, many consumers encounter two commonly confused models: LR44 and 357. Despite looking nearly identical, they serve slightly different purposes due to their chemical c…

-
LR44 Battery Equivalent And Replacement
What is the LR44 battery – this is a 1.5 V alkaline button cell battery commonly used in small electronic devices such as calculators, small remote controls, etc.

-
CR1616 Battery Equivalent: What Battery is Equivalent to CR1616?
This post covers all you need to know about the CR1616 battery and what makes it different, as well as any original batteries that work the same.

-
LR44 Equivalent Batteries - A Simple Guide
Learn what batteries can replace CR1616 safely. We compare size, voltage, and performance to help you choose the right one.

-
LR44 vs AG13: Are They the Same? Differences, Compatibility, and Equivalents
LR44 vs AG13: Are They the Same?When buying button cell batteries, LR44 and AG13 are two of the most common models people encounter. Due to their identical size and similar labeling, many wonder if th…
Stock: 227,125
Unit Price:$0
Ext Price:$0
| Qty. | Unit Price | Ext Price |
| 1+ | $0.150000 | $0.150000 |
| 50+ | $0.130000 | $6.500000 |
| 500+ | $0.110000 | $55.000000 |
| 1000+ | $0.090000 | $90.000000 |
| 4000+ | $0.070000 | $280.000000 |
| 8000+ | $0.060000 | $480.000000 |
| 24000+ | $0.055000 | $1320.000000 |
Inventory:227,125
Send us your inquiry,we will respond immediately.

-
NCU15XH103F6SRC
Murata Electronics

-
ERT-JZEG103FA
Panasonic Electronic Components
.jpg)
-
ERT-J0EM103J
Panasonic Electronic Components

-
NTCG103JF103FT1
TDK Corporation

-
NTCG104EF104FT1X
TDK Corporation
-
ERT-J0ER103J
Panasonic Electronic Components

-
NCP15XH103F03RC
Murata Electronics
-
NCP03WF104F05RL
Murata Electronics

-
ERT-J0EG103FA
Panasonic Electronic Components

-
NCP15WB473F03RC
Murata Electronics

-
NCP15XH103J03RC
Murata Electronics
-
ERT-J1VR103J
Panasonic Electronic Components
.jpg)
-
B57232V5103F360
EPCOS - TDK Electronics

-
NCU18XH103F6SRB
Murata Electronics

-
NCU18XH103F60RB
Murata Electronics

-
ERT-J1VS104FA
Panasonic Electronic Components

-
NCP21XV103J03RA
Murata Electronics

-
NCP18XH103J03RB
Murata Electronics

-
NCP18XH103F03RB
Murata Electronics

-
NCU18WF104F6SRB
Murata Electronics
Latest News
- SEMITEC China distributor,in-stock inventory,fast trading
-
2019.09.09
For more information about SEMITEC thermistors and constant current diodes, please contact Bomkey Electronics.As the authorized distributor, we supply the full range of SEMITEC (Ishizuka) products.
- Taiwan's First MEMS Pressure Sensor Manufacturer — Metrodyne Microsystems
-
2019.09.11
Bomkey Electronics Co., Ltd. is the authorized distributor of the full range of Metrodyne pressure sensors.
- The core components of data storage and information perception
-
2025.01.15
In today's era of rapid digital information development, memory and sensors are like the "memory center" and "sensing antenna" of electronic devices, respectively, shouldering the important mission of …
- Master of precision regulation of electronic signals
-
2025.01.15
In today's complex and ever-changing field of electronic technology, oscillators, resonators, and filters are like highly skilled masters. They play an indispensable role in many electronic devices and…
- Security Guard and Energy Steward of Electronic Systems
-
2025.01.15
In today's highly electronic era, circuit protection and power management are like two solid pillars of an electronic system. The former is like a loyal guard, always alert to various abnormal situatio…
- Key "valves" and "switches" in the electronics world
-
2025.01.15
In the large family of electronic components, diodes, transistors, and thyristors are like delicate "valves" and "switches" that control the path and flow of electronic flow, and are the core elements …
- The Cornerstone and Power Source of Electronic Circuits
-
2025.01.15
In the vast world of electronic technology, resistors, capacitors, and magnetic devices are like three solid cornerstones that together build a high-rise building of electronic circuits and provide an …
- How to Read a 2.2K Resistor: Color Code, Identification, and Practical Use
-
2025.06.24
How to Identify 2.2K Resistor: Color Code, Circuit and ApplicationsIf you're working with electronics, you need to know how to read resistors. 2.2k ohm resistor: Probably the most used resistor in ci…
- 100 Ohm Resistor Color Code Guide
-
2025.06.19
What Is a 100 Ohm Resistor?The 100 ohm resistor holds a prominent place among electronic components due to its wide range of applications and ease of use. Its frequent appearance in electronic circuit…
- 357/303 Battery Equivalent: Interchangeability, Differences & Best Replacements
-
2025.06.19
Explore the differences and similarities between 357 and 303 batteries. Understand their equivalents, compatibility, voltage, and the best replacements for watches, calculators, and medical devices.
- What is a 100 Ohm Resistor? Color Code,Uses and Everything You Should Know
-
2025.06.03
100 ohm resistor is a passive electrical component that resists the flow of current by 100 ohms. In simple terms, it acts like a speed bump for electricity - slowing down the current to protect other c…
- Electronic Signal Enhancement and Rhythm Controller
-
2025.01.15
In the complex symphony of electronic technology, amplifiers and clock circuits play the key roles of "loudspeakers" for signal enhancement and "conductors" for rhythm control, respectively. They coope…



