What is a 100 Ohm Resistor? Color Code,Uses and Everything You Should Know
Resistors are the most common components in any electronic circuit, and among them, the 100 ohm resistor is a particularly popular one. From protecting LEDs to shaping signal behavior, it's a staple of both hobbyist kits and professional designs. In this article, we'll walk you through what a 100 ohm resistor is, how to read its color code, its applications, and how it fits into the EIA standard values.
What is a 100 Ohm Resistor?
100 ohm resistor is a electric component with a resistance of 100 ohm. In layman's terms, it works like a speed bump to electricity, slowing the current down to guard other elements in a circuit.It's called the ohm, after Siemens' rival the 19th century's German physicist Georg Ohm, and it tells us electrical resistance. When voltage there is applied it allows an amount of current to flow according to Ohm's law current = voltage / resistance Current = 5V / 100 ohm 50mA(flow) 10-2A(flow) percentage current(0.05* 10^-2* 100)% 0.05 proportion of current belew 50% 0.05 = 5% portion of time below the current 50% (4)The amount of current varies over time, when the percentage of time is at the current fairly long the average current will realy near to the current.
V = I × R
So, If 5 volts are applied to a 100 ohm resistor, the current that will pass through is:
I = V / R = 5V / 100Ω = 0.05A or 50 mA
This makes them helpful for limiting current in LED lights, sensors, or micro controller I/O pins.
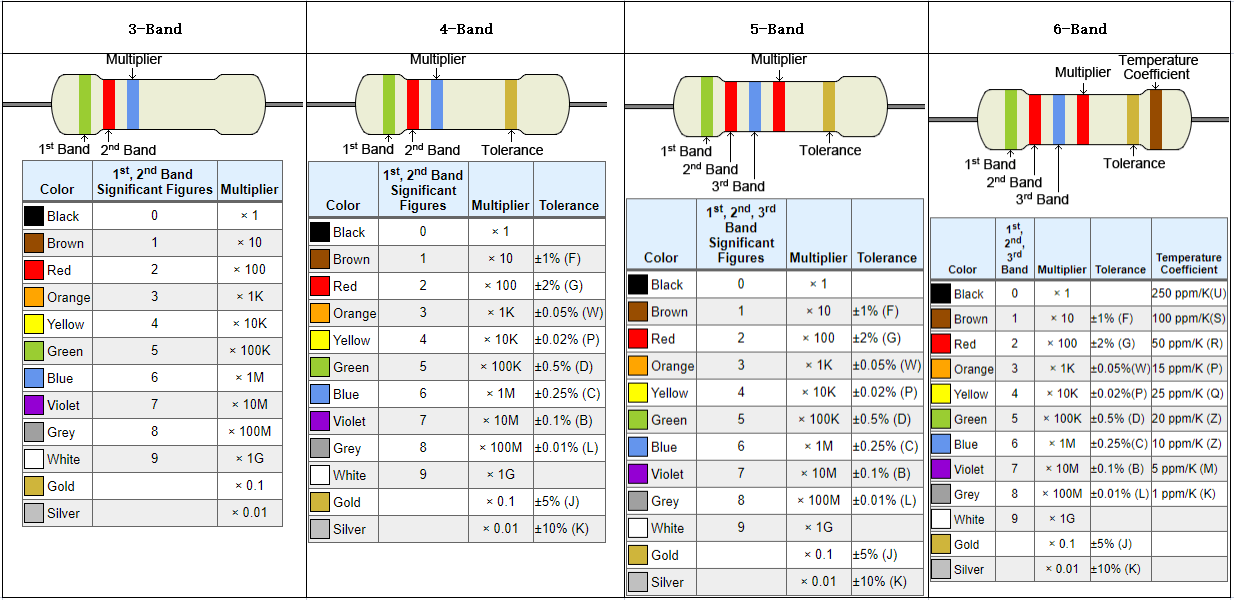
100 Ohm Resistor Color Code
Most resistors use colored bands to indicate their resistance. A 100 ohm resistor typically has the following 4-band color code:- 1st Band (Digit 1): Brown = 1
- 2nd Band (Digit 2): Black = 0
- 3rd Band (Multiplier): Brown = ×10
- 4th Band (Tolerance): Gold = ±5%
➡ Brown – Black – Brown – Gold
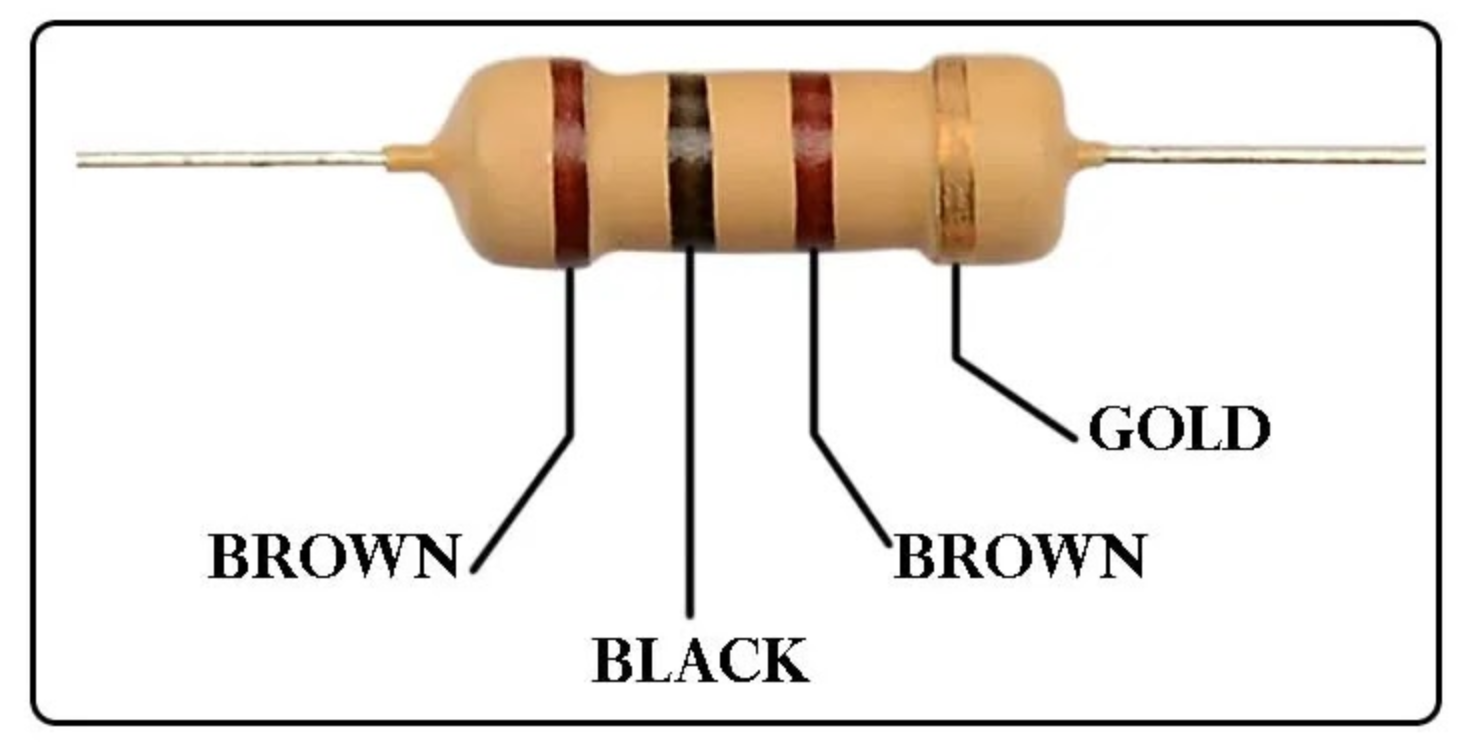
100 Ohm Resistor Color Code for 4-band
How to Read the 100 Ohm Resistor Color Code
To decode the color bands, follow this step-by-step method:
1.Start from the left side (usually the band nearest the edge).2.Read the first two color bands as digits.
3.The third band is the multiplier - it tells you how many zeros to add.
4.The fourth band is tolerance, which indicates manufacturing precision.
Using our example:
- Brown (1)
- Black (0)
- Brown (×10)
- Gold (±5%)
→ Combine the digits: 10 × 10 = 100 ohms
Resistor Color Code Explained
Color coding is a universal standard to make resistor values readable without text labels, especially for small components. Here's a quick reference for digits and multipliers:
| Color | Digit | Multiplier |
|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | ×1 |
| Brown | 1 | ×10 |
| Red | 2 | ×100 |
| Orange | 3 | ×1,000 |
| Yellow | 4 | ×10,000 |
| Green | 5 | ×100,000 |
| Blue | 6 | ×1M |
| Violet | 7 | ×10M |
| Gray | 8 | ×100M |
| White | 9 | ×1G |
| Gold | – | ×0.1 |
| Silver | – | ×0.01 |
Applications of 100 Ohm Resistor
The 100 ohm resistor is extremely versatile and is used in various real-world applications:Current Limiting for LEDs
Too much current can burn out an LED. A 100 ohm resistor is often used in series to limit the current to a safe level.Voltage Division
When used with another resistor in a series, it can divide voltage - useful for feeding signals into analog sensors or ADCs.Pull-Up/Pull-Down Resistors
Although 10k is more common, 100 ohm resistors are sometimes used in low-impedance systems to pull signals to ground or Vcc.Impedance Matching
In communication systems, such as RS-485 or CAN Bus, 100 ohm termination resistors help prevent signal reflection.SMD Circuit Design
In surface mount circuits, SMD resistors with marking "101" represent 100 ohms and are widely used for compact PCB layouts.Standard EIA Decade Resistor Values
Resistors are manufactured in standard series defined by EIA (Electronic Industries Alliance). These include:- E6 Series: 20% tolerance – values like 100, 150, 220 ohms
- E12 Series: 10% tolerance – adds 120, 180, 270, etc.
- E24 Series: 5% tolerance – more granular values
- E96/E192 Series: 1% and 0.5% tolerance – very precise
The 100 ohm resistor appears in all series, making it a universal value that's easy to source and apply across many designs.
Conclusion
The 100 ohm resistor might seem small, but it plays a vital role in modern electronics. Whether you're building a blinking LED circuit, fine-tuning signal levels, or designing a complex microcontroller-based project, chances are - you'll need one.Understanding how to read its color code, apply it in circuits, and choose the right tolerance and size will help you become more confident in your electronics journey. It's a small component with a big impact - and a must-have in every toolkit.